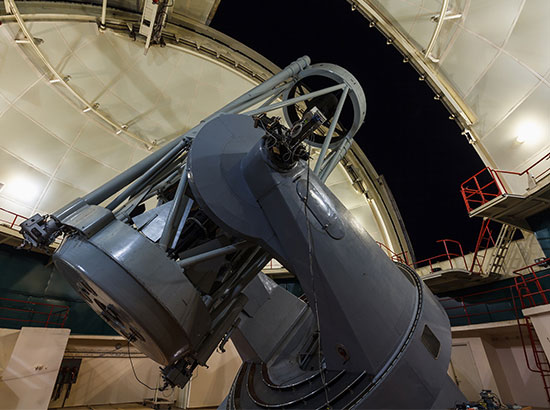
Widely used in astronomy and space, from telescope manufacturing to space exploration
Firstly, in the field of astronomy, the application of optical components is mainly reflected in the manufacturing of telescopes. Telescopes use optical filters, lenses, and prisms to select and focus light of specific wavelengths, thereby observing and studying the spectral characteristics and motion patterns of celestial bodies such as stars, planets, and galaxies. For example, optical filters are used in stellar spectroscopy to select specific wavelengths of light, allowing for the study of the spectral characteristics of stars. Additionally, telescopes utilize reflective or catadioptric techniques, combining lenses and mirrors to achieve celestial observations. This method offers advantages such as large apertures and no chromatic aberration, but it is complex in structure and costly to manufacture.
In the space field, the application of optical components is equally important. Space optics, as a branch of science that uses optical equipment to observe and study space and Earth, employs different bands and types of optical equipment to receive visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, and soft X-rays from celestial bodies. This allows for the detection of their presence, determination of their positions, study of their structures, and exploration of their motion and evolution patterns. Space optical systems are developing towards large apertures, long focal lengths, wide fields of view, multi-spectral capabilities, high measurement accuracy, and lightweight designs to meet the demands of space exploration.
In summary, the application of optical components in the fields of astronomy and space not only advances astronomical research but also provides crucial technical support for space exploration. From the ground to space, from the microscopic to the macroscopic, the role of optical components is indispensable.