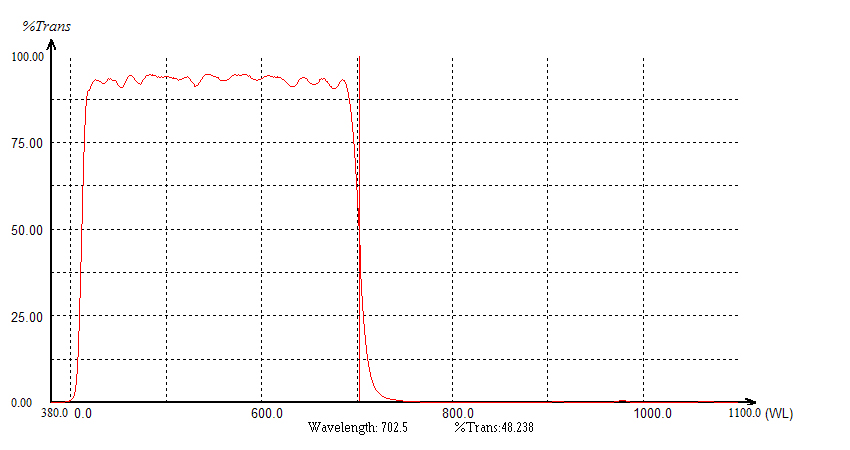
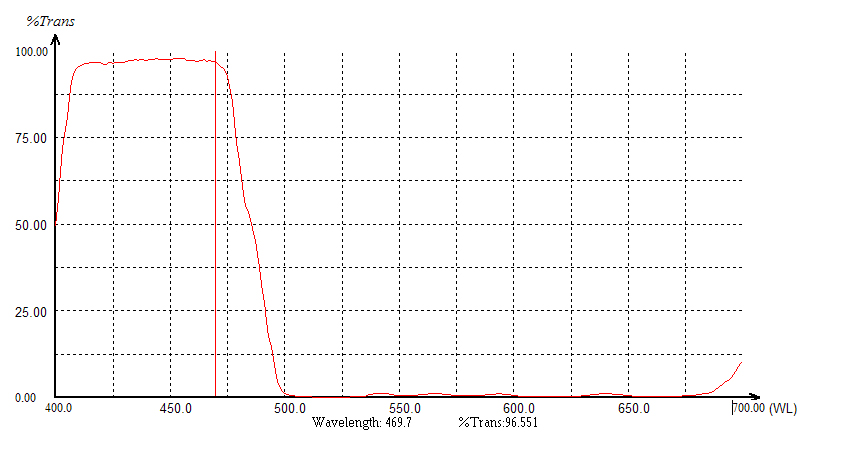
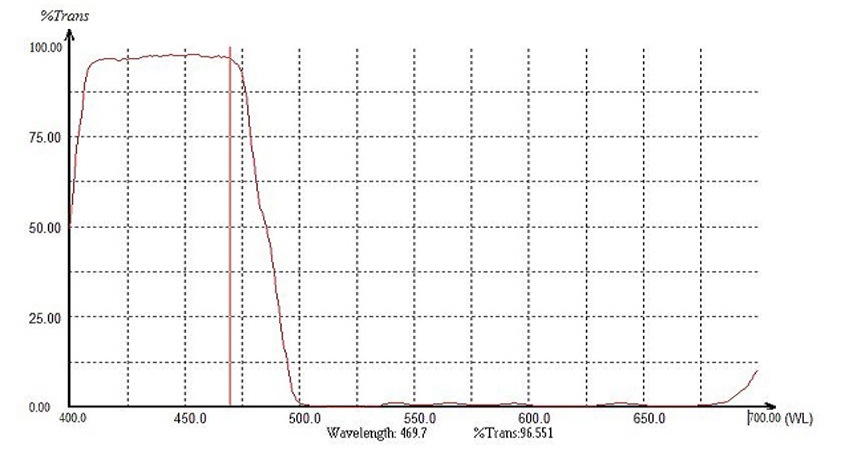
The short pass filter is to transmit shorter wavelengths of light while rejecting longer wavelengths. The design of this type of filter makes it easier to separate excitation and emission wavelengths within the desired range, effectively isolating longer wavelength light without interfering with specific wavelengths.
High Transmittance: Short pass filters have high transmittance and high cut-off depth, with transmittance typically reaching over 90%.
High Cut-off Steepness: These filters have a narrow cut-off bandwidth and high cut-off steepness, effectively separating excitation and emission wavelengths without interfering with the wavelengths of interest.
High Background Light Density: They possess a high background light density, effectively reducing background light interference.
Material Diversity: Short pass filters can be made from materials such as UV fused silica or optical-grade float glass, offering different transmission characteristics and cut-off wavelengths.
Fluorescence Excitation Spectroscopy: Used to eliminate interference light outside the usable wavelength band, improving imaging clarity and system sensitivity.
Raman Spectroscopy Applications: Crucial for noise reduction in spectra and isolating specific spectral regions.
Imaging Optical Systems: Enhances imaging clarity and system sensitivity.
Machine Vision Systems: Used to eliminate interference light outside the usable wavelength band, improving system performance.
Other Applications: Beauty instruments, high-intensity flashlights, stage lighting gels, facial recognition attendance devices, optical instruments, fiber optic lighting, halogen lamp heat insulation sheets, cold light source display cabinets, and police multi-band detection instruments.