Dichroic filters are devices that can filter or block light to ensure that image colors appear normal. They primarily transmit wavelengths that are either longer than a starting wavelength or shorter than a cut-off wavelength, and they can be categorized into long pass filters and short pass filters. Dichroic filters are widely used in applications such as fluorescence excitation spectroscopy, beam splitting, and beam combining.
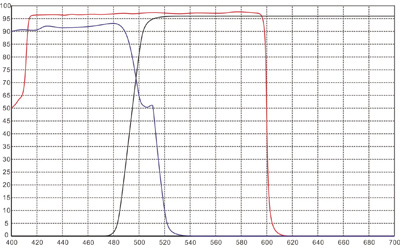
Wavelength Selectivity: Dichroic filters can almost completely transmit light of specific wavelengths while almost completely reflecting light of other wavelengths. This characteristic allows dichroic filters to effectively separate and transmit light of specific wavelengths.
Angle Sensitivity: Unlike absorptive filters, dichroic filters are highly sensitive to the angle of incident light. The transmission and reflection rates of the filter change when light enters at different angles. Therefore, special attention must be paid to the angle of incident light during use.
High Transmittance and Low Absorption: Dichroic filters are designed to transmit specific wavelengths of light while reflecting others. This design reduces light absorption, thereby minimizing heat generation and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Versatile Applications: Dichroic filters are widely used in laser technology, imaging, spectral analysis, beam splitting, and beam combining. They provide high transmittance and high reflectance, making them suitable for various optical systems.
Laser Technology: Dichroic filters are widely used in laser technology to effectively separate, transmit, or reflect specific wavelengths of light, thereby improving light utilization and color saturation.
Imaging and Spectral Analysis: In imaging and spectral analysis, dichroic filters are used in hyperspectral imaging spectrometers and hyperspectral cameras to achieve high-precision spectral classification and imaging.
Optical Instruments and Devices: Dichroic filters are used in optical instruments such as projectors, scanners, and fluorescence microscope systems for beam splitting and combining, enabling multifunctional optical path designs.
Biological and Chemical Analysis: In precision optical systems like biological fluorescence systems and Raman systems, dichroic filters are used for fluorescence excitation spectroscopy, beam splitting, and combining, thereby improving the accuracy and efficiency of analysis.