The aspheric surface can correct the system aberration and improve the image quality in the optical imaging system, in addition to that it can simplify the system structure significantly; On the other hand, the resolution of imaging system can be increased by improving the system aperture. Therefore, in the domain of basic scientific research, astronomical cosmological exploration and military defense security, the large-aperture aspheric mirrors are all highly required.
Characteristics and Challenges of Large-Diameter Aspheric Processing
Aspheric surfaces have only one axis of symmetry, making it impossible to use traditional lapping methods for grinding.
The radius of curvature varies at different points on an aspheric surface, making shape correction difficult.
The inspection methods for aspheric surfaces are very complex and cannot simply use templates to check the aperture.
The manufacturing of large-diameter optical aspheric mirrors is a complex and lengthy process with a long cycle time. The process mainly includes milling and shaping, aspheric grinding, rough polishing, fine polishing, and coating. Each process step must be equipped with one or more corresponding inspection methods to ensure the efficient operation of the process. The key stages in the processing of large-diameter aspheric optical elements are grinding and polishing.
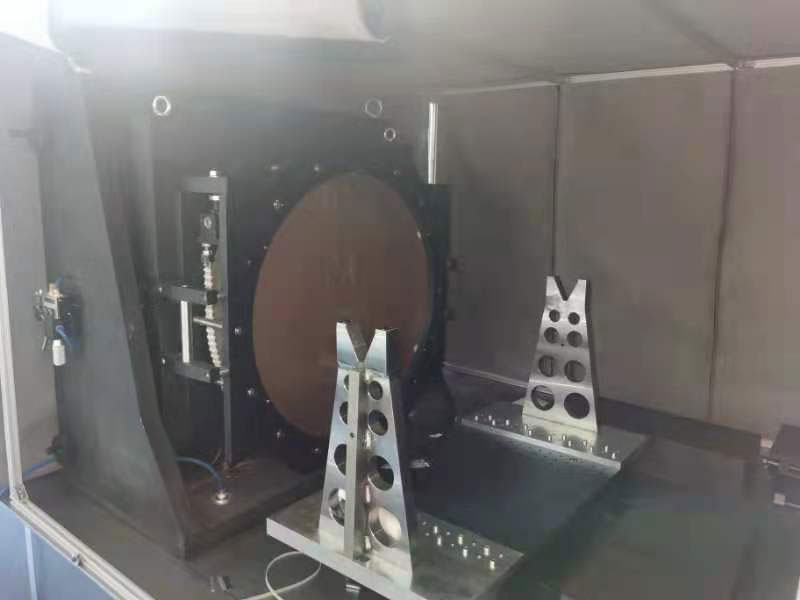
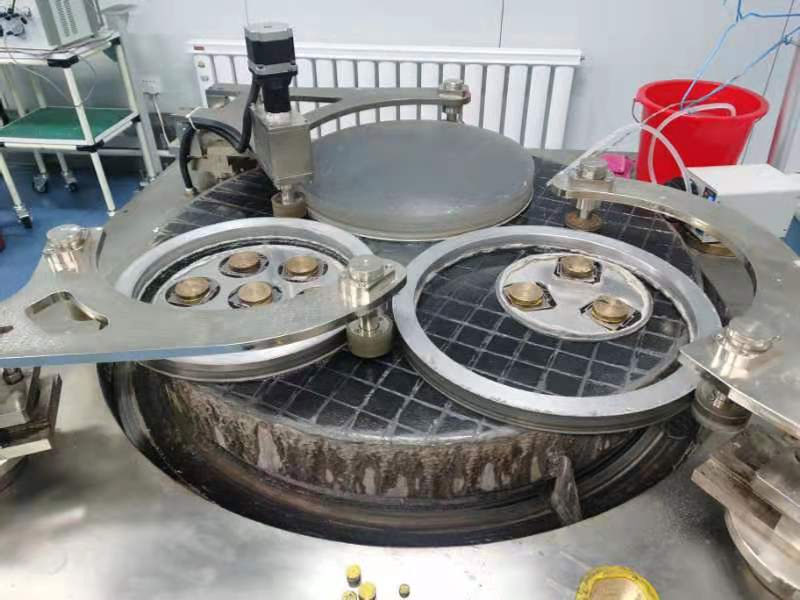
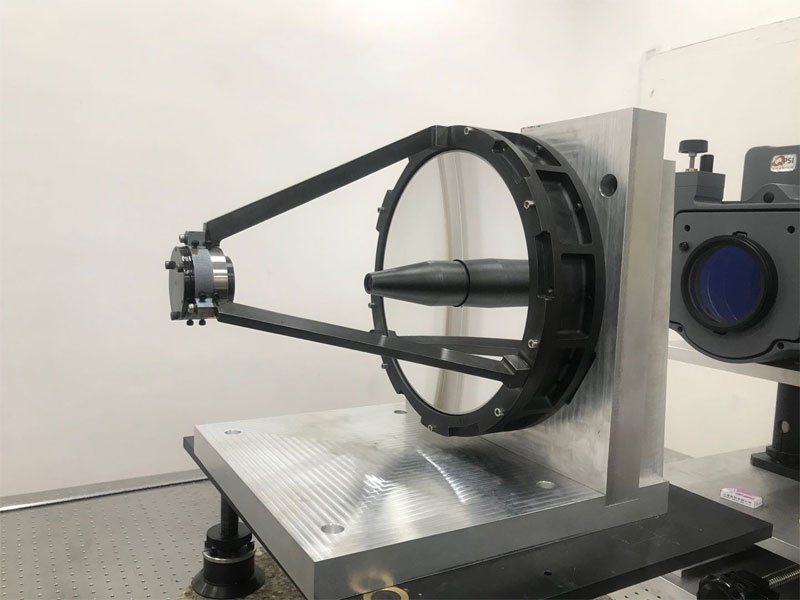



Bena Optics offers precision-ground large-diameter aspheric lenses. The larger diameter provides superior light collection and focusing specifications. These lenses are made from low dispersion materials to minimize chromatic aberrations. Lenses with diameters more than 15 mm have a corrected wavefront transmission that is typically 20 to 50 times better than the equivalent molded glass aspheric lenses.