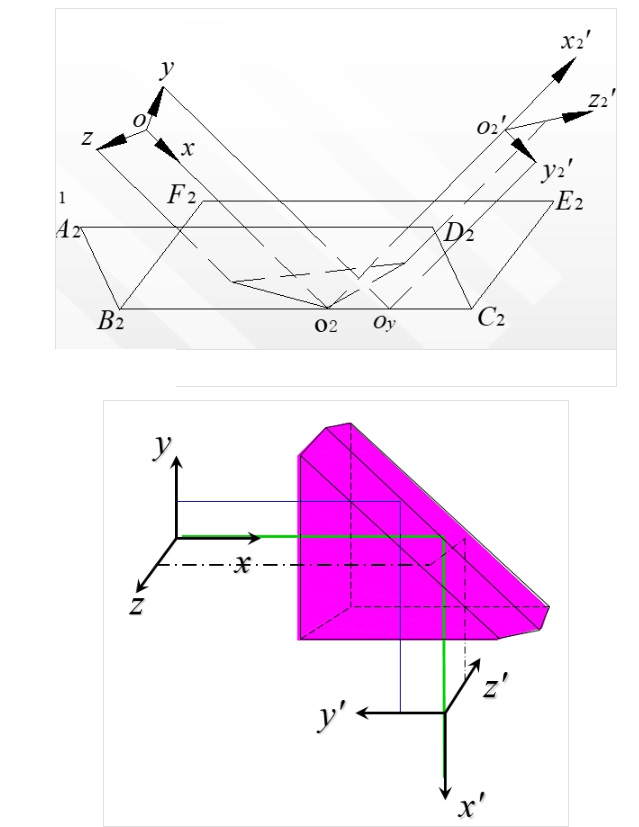
The roof prism is a type of prism with two mutually perpendicular reflective surfaces. This prism can deflect light by 90 degrees and is not limited by the critical angle of total internal reflection, allowing it to accept incident light at larger angles. Roof prisms are relatively small in size and are commonly used in very compact binoculars because they allow the objective lens and the eyepiece to be aligned in a straight line.
The key feature of a roof prism is the presence of a roof surface. The so-called roof surface is a reflective surface in the light path that is formed by two reflective surfaces meeting at a ridge. The edge of these two surfaces lies right in the middle of the light path, which is why some roof prisms have a visible dividing line in the center. Essentially, it can be understood as splitting the light beam into two halves and then recombining them. By arranging two mirrors at a right angle, a roof surface is formed. A commonly used Pechan prism, for example, requires six reflections.
Specifications | Commercial spec. | High precision spec. |
Material | UV glass (Quartz, Fused silica) VIS glass (Schott, CDGM, HOYA, etc.) IR material: (Sapphire, ZnSe, Silicon, etc.) Special material: (SiC) | |
Dimension | 5mm~100mm | |
Dimension tolerance | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
Surface quality | 60/40 | 40/20 |
Surface flatness | 1/4λ | 1/10λ |
Clear aperture | >85% of dim | >90% of dim |
90°Deviation tolerance | 3 arc min | 5 arc sec. |
Bevel | <0.2mm x 45deg | <0.1mm x 45deg |
Coating | Up on clients’ request | |
Type No. | Dimension (mm) | Tolerance of roof angle | Material | |
A | B | |||
RP-18-24.5-5 | 18 | 24.5 | ±5 arc sec. | BK7 / Fused silica |
RP-18-24.5-15 | 18 | 24.5 | ±15 arc sec. | BK7 / Fused silica |
RP-32-41-5 | 32 | 41 | ±5 arc sec. | BK7 / Fused silica |
RP-32-41-15 | 32 | 41 | ±15 arc sec. | BK7 / Fused silica |
Telescopes: Telescopes that use a roof prism structure are typically referred to as ROOF prism telescopes. Due to their complex structure and high manufacturing requirements, they are usually applied in high-end telescopes. Roof prisms allow the objective lens and the eyepiece to be aligned in a straight line, making them ideal for very compact binoculars.
Microscopes: Roof prisms are used to convert the real image formed by the objective lens into a virtual image that can be observed through the microscope, thereby enhancing magnification and the field of view.
Lasers: Roof prisms are used to reflect and focus the laser beam to a single point, forming a high-energy laser beam.
The characteristics of roof prisms include their small size and the ability to align the objective lens and the eyepiece in a straight line, making them suitable for very compact optical devices. Additionally, the manufacturing process for roof prism is demanding, and they are typically used in high-end products.