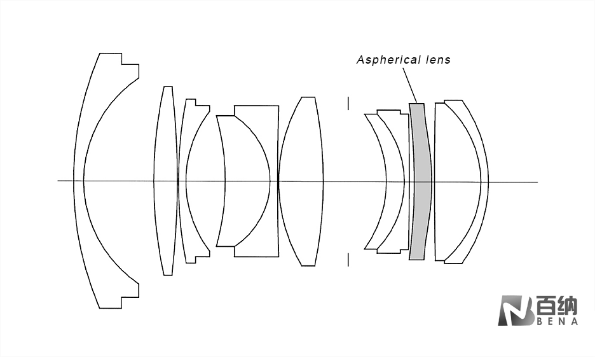
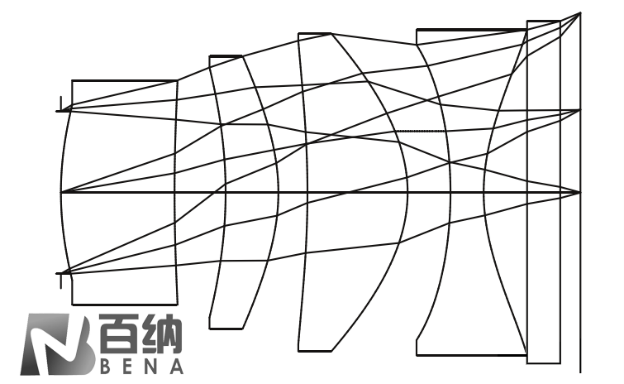
In optical systems, the most used spherical lenses have surfaces that are rotationally symmetric spherical surfaces, meaning they have a constant curvature from the center to the edge of the lens. In contrast, aspheric lenses have surfaces that are rotationally symmetric but not spherical, conforming to specific mathematical expressions and having smooth, continuous surfaces.
There are three main types of aspheric surfaces used in optical systems: the first type is axisymmetric aspheric surfaces, such as rotational conic surfaces and higher-order rotational surfaces; the second type is aspheric surfaces with two planes of symmetry, such as cylindrical surfaces and toroidal surfaces; the third type is freeform surfaces, which have no symmetry.
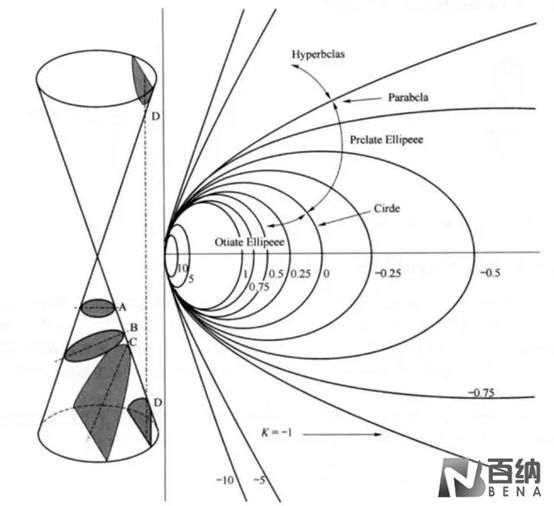
The most commonly used aspheric surface expression is constructed by taking a conic surface as the base and then superimposing a series of higher-order polynomials. The expression is:
[ z® = \frac{r^2}{R \left(1 + \sqrt{1 - (1 + k) \frac{r2}{R2}}\right)} + \sum_{i=2}^{n} A_i r^i ]
where:
1. ( z® ) is the height of the lens surface at a radial distance ( r ).
2. ( R ) is the radius of curvature of the base sphere.
3. ( k ) is the conic constant (also known as the eccentricity constant).
4. ( A_i ) are the coefficients of the higher-order polynomial terms.
5. ( r ) is the radial distance from the optical axis to the point on the surface.
This expression combines a basic conic surface (defined by ( R ) and ( k )) with a series of higher-order polynomial terms (defined by the coefficients ( A_i )) to accurately describe the shape of the aspheric lens.
Spherical lenses, regardless of any measurement or manufacturing errors, inherently exhibit spherical aberration. The most notable advantage of aspheric lenses is their ability to minimize aberrations by adjusting and optimizing the conic constant and aspheric coefficients. As shown in Figure 3, a spherical lens with significant spherical aberration is compared to an aspheric lens with almost no spherical aberration. In comparison, a single aspheric lens achieves better image quality.
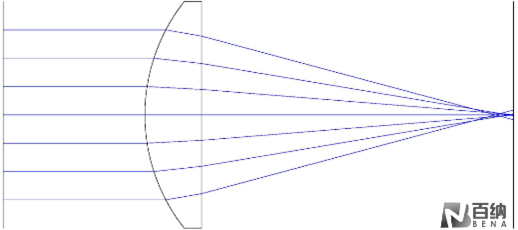
Illustration of Spherical Aberration in a Spherical Lens
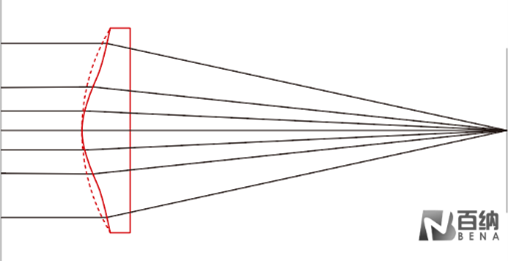
Spherical Aberration Correction in an Aspheric Lens
Compared to the conventional method of correcting spherical aberration by increasing the number of lenses, aspheric lenses can achieve better aberration correction with fewer lenses. For example, a zoom lens that typically uses ten or more lenses can achieve the same or higher optical performance by replacing five or six spherical lenses with one or two aspheric lenses, thereby reducing the system’s length and complexity.
Additionally, optical systems with more optical elements often have strict mechanical tolerance requirements, which can lead to additional calibration steps and more anti-reflective coatings, reducing the overall practicality of the system. Therefore, the use of aspheric lenses in optical systems (despite their higher cost compared to single-element lenses and cemented doublets with equivalent F-numbers) can lower the overall system cost.
In summary, the reasonable use of aspheric lenses in optical systems holds an irreplaceable position in achieving miniaturization, lightweight, and multifunctionality of optical systems.
Aspheric lenses from aspheric lenses manufacturers play a very important role in optical systems. For example, in the complex systems we frequently encounter, such as smartphone lenses, camera lenses, and ultra-short throw projectors, the optimization of system aberrations is often achieved by combining multiple aspheric and spherical lenses. These systems are typically not standardized products.