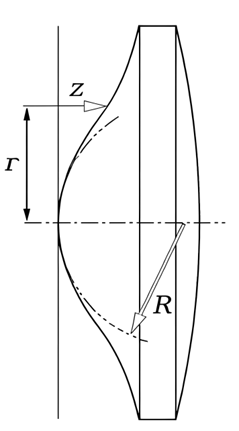
Aspherical lenses do not have a simple spherical surface; instead, they have a rotationally symmetric, smooth, and continuous aspheric surface that conforms to a specific expression. This design allows light to travel through the lens in a more ideal path, thereby reducing aberrations and improving image quality. The radius of curvature of an aspheric lens changes along the central axis, which can enhance optical quality, reduce the number of optical elements needed, and lower design costs.
Eliminating Spherical Distortion: Aspherical lenses can effectively reduce or eliminate distortions at the edges of spherical lenses by optimizing the surface shape, thereby improving image quality.
Enhanced Focusing Ability: Aspherical lenses can be custom-shaped to focus light into smaller spots, making them particularly suitable for applications like laser focusing and optical communications.
Flat Light Field: Aspherical lenses provide a flatter light field, maintaining good image quality even at large off-axis angles, which is ideal for lighting systems and projectors.
Multifocal Function: By adjusting the surface shape, aspheric lenses can achieve multifocal functionality, focusing different wavelengths of light at different focal points, useful for spectral imaging and measurement.
System Miniaturization and Weight Reduction: Using aspheric lenses can simplify optical system design, reduce the number of required lenses, and thereby decrease the system’s size and weight.
Specifications | Commercial spec. | High precision spec. |
Material | UV glass (quartz, fused silica) | |
VIS glass (Schott, CDGM, HOYA, etc.) | ||
Diameter | Ø5mm~Ø600mm | |
Diameter tolerance | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
Focal length tolerance | ±2% | ±1% |
Surface quality | 60/40 | 40/20 |
Centration | < 3 arc min | <1arc min |
Surface accuracy | RMS <λ/60 | RMS<λ/150 |
Surface irregularity | 1/4λ | 1/10λ |
Clear aperture | >85% of dia | >90% of dia |
Bevel | <0.2mm x 45deg | <0.1mm x 45deg |
Coating | Up on clients’ request | |
Optical Instruments: Aspherical lenses are widely used in telescopes, microscopes, and optical measurement devices to improve image quality and measurement accuracy by reducing spherical aberrations.
Laser Systems: Aspherical lenses excel in laser systems for applications like laser collimation, processing, cutting, and welding, optimizing beam shape and divergence to enhance focusing efficiency and precision.
Fiber Optic Communication Systems: In optical modules, aspheric lenses improve signal strength and stability, reduce focal spot size, and enhance transmission quality and distance. They also minimize mode interference and crosstalk.
Imaging Systems: Aspherical lenses are crucial in large-aperture, wide-angle, fisheye, and zoom lenses, reducing edge distortions and improving image quality in devices like night vision goggles and thermal imagers.
Automotive Optical Systems: Used in headlights and onboard cameras, aspheric lenses improve light distribution and image quality, enhancing nighttime driving safety.
Medical Ophthalmology: Aspherical lenses in eyeglasses and contact lenses correct refractive errors, providing clearer vision.
Lighting Systems: Aspheric lenses offer a flatter light field and maintain image quality at large off-axis angles, making them ideal for lighting systems and projectors.
Multifocal Function: By adjusting their surface shape, aspheric lenses can focus different wavelengths at different points, useful for spectral imaging and measurement.