The working principle of a laser scanning galvanometer is based on the generation of torque by an electromagnetic coil in a magnetic field. By controlling the magnitude and direction of the current, the rotation angle of the mirror can be precisely controlled, thereby changing the direction of the reflected laser beam. The galvanometer primarily consists of two mirrors (X-axis and Y-axis), each controlled by a different motor, allowing for high-precision deflection movements under computer commands.
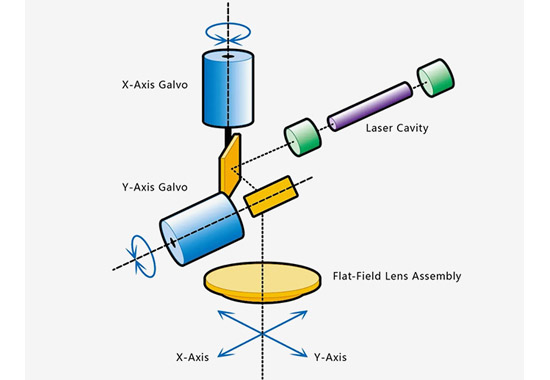
The working process of a laser scanning galvanometer includes the following steps: First, the laser beam is incident on the mirror. The mirror deflects along the X-axis and Y-axis, causing the laser beam to deflect accordingly. By controlling the angle of the mirror, the laser scanning mirror focus point can be precisely moved on the material surface according to a preset pattern or text. This marking method not only leaves permanent and clear marks on the material surface but also allows the shape of the focused laser spot to be adjusted as needed. Whether a circular or rectangular spot is required, it can be easily achieved.
Scanning galvo mirror systems marking heads have a wide range of applications and flexible marking methods, capable of meeting various complex marking needs. They support vector graphics and text marking, offering high drawing efficiency and excellent graphic precision. They also support dot matrix marking, suitable for online marking scenarios, and can record more information points. With their high precision, high speed, and flexibility, galvanometer scanning marking heads have become the mainstream products in the current laser marking field.
Bena Optics supplies a variety of laser scanning galvanometers made from different materials, including
optical glass, fused silica, silicon, silicon carbide, and metals such as beryllium. Additionally, they can process various thin film coatings to meet the needs of different laser scanning systems.