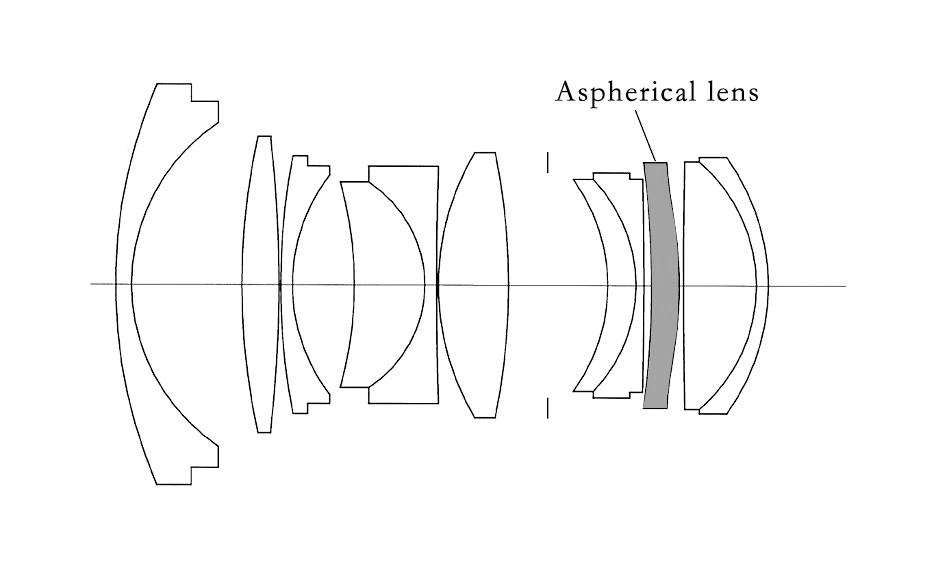
Aspheric lenses play a crucial role in optical systems. For example, in complex systems such as smartphone lenses, camera lenses, and ultra-short throw projectors, multiple aspheric and spherical lenses are often combined to optimize system aberrations, without forming standardized products.
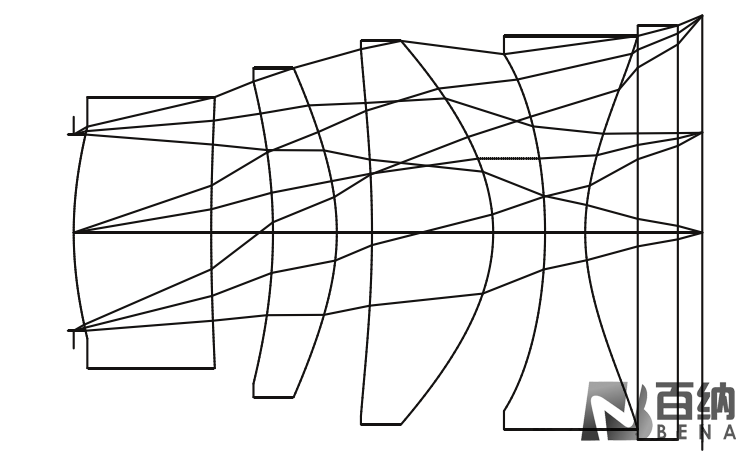
Another significant application of aspheric lenses is in laser collimation, focusing, and coupling lasers with optical fibers. The light beam directly emitted from a laser is typically a Gaussian beam. However, in practical applications such as optical measurement, laser medical treatment, and laser processing, the laser beam needs to be collimated, focused, and homogenized. Conventional methods using spherical lenses for collimation usually require at least two lenses.
Since lasers are monochromatic light sources, spherical aberration often hinders a single spherical lens from achieving diffraction-limited performance when focusing or collimating light. A single aspheric lens, which optimizes spherical aberration, perfectly addresses this issue. Therefore, aspheric lenses are commonly used to collimate the output light from optical fibers or laser diodes and to couple lasers into optical fibers.
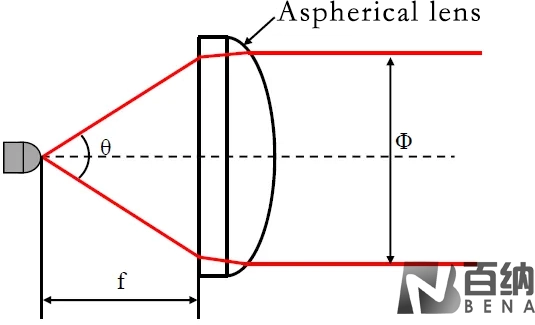
When using an aspheric lens from the professional aspheric lenses manufacturers for laser collimation, the flat surface, i.e., the surface with a larger radius of curvature (sometimes a plane), should face the laser source. Assuming the divergence angle of the light source is θ and the required collimated beam diameter is Φ, the focal length of the aspheric lens suitable for this system can be calculated.
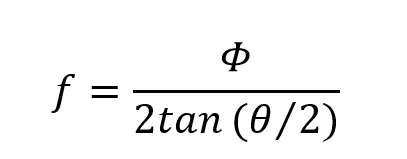
Additionally, the numerical aperture (NA) of the light source should be smaller than the numerical aperture (NA) of the aspheric lens. For example, for a laser diode with a wavelength of 650nm and an emission angle of 30°, if the collimated beam diameter is 3mm, the required focal length of the aspheric lens can be determined.
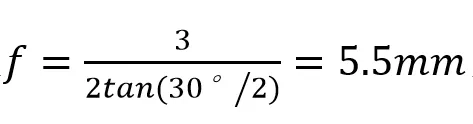
In fields such as industrial processing, optical measurement, and laboratory research, the parameters of commonly used laser sources and optical fiber sources, such as wavelength, divergence angle, and collimated beam diameter, are relatively well-defined. Therefore, Bena Optics has designed and produced a series of high-performance, precision-polished large-diameter aspheric lenses and precision-molded glass aspheric lenses for these applications. These lenses are widely used in laser collimation, focusing, and coupling lasers with optical fibers.