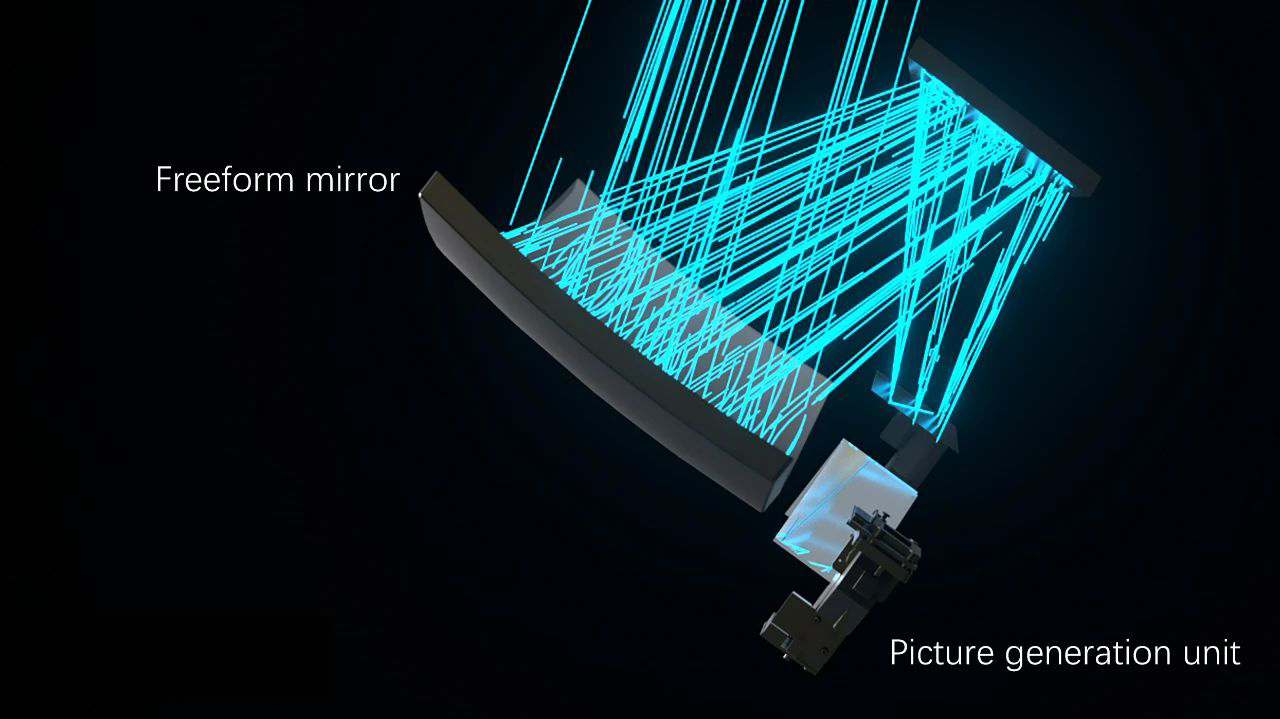
Optical freeform surfaces can achieve functionalities in optical systems that are difficult to realize with traditional spherical or aspheric surfaces alone. They require fewer components, making the entire optical system smaller, lighter, and more efficient. This meets the modern demands for high performance, lightweight, and miniaturized optical systems. Therefore, freeform optical elements have widespread applications across various fields, primarily categorized into three areas: imaging, illumination, and display.
In the imaging field, freeform surfaces are widely used in astronomical observation and space optical systems. Recently, some smartphone lenses have also incorporated freeform surfaces to achieve automatic distortion correction.
In the illumination field, freeform surfaces play a crucial role in the structural design of streetlights and automotive headlights. They increase the effective illumination range and improve energy utilization efficiency.
In the display field, freeform surfaces are indispensable in systems such as head-mounted displays and micro-projectors. They contribute significantly to the performance and compactness of these devices.
By leveraging the unique advantages of free form optics surfaces, optical systems can achieve higher performance and efficiency, driving innovation across multiple industries.

Freeform surfaces can be applied in both transmissive lenses and reflective mirrors. For example, in Head-Up Displays (HUDs), freeform surfaces are commonly used in reflective optics. The optical design requirements for HUDs are quite complex:
1. Image Magnification and Field of View (FOV): The optical system needs to magnify the optical image and project it to the required imaging distance (VID) while meeting the FOV requirements.
2. Image Clarity: The system must ensure high image clarity and resolution.
3. Windshield Matching: The design must match the shape of the car’s windshield, controlling parameters such as static distortion, dynamic distortion, and binocular disparity to low levels.
Additionally, by leveraging the design flexibility of freeform surfaces, it is possible to eliminate HUD ghosting.
Given these complex design requirements, traditional spherical or symmetric aspheric surfaces are no longer sufficient. The need for higher design freedom necessitates the use of freeform optics design, which also demands advanced optical design capabilities.
Freeform surfaces offer the flexibility and precision needed to meet the stringent requirements of modern optical systems, such as HUDs. They enable the design of more efficient, compact, and high-performance optical components, driving innovation and improving user experience across various applications.