Telecentric lenses are renowned for their unique capabilities, particularly in applications requiring precise measurements and stable imaging. These lenses offer several key advantages that set them apart from conventional optical systems.
In metrology applications, it is often necessary to capture orthographic views of objects (i.e., without perspective distortion) to perform accurate linear measurements. However, many mechanical components cannot be precisely positioned due to factors such as vibration or may need to be measured at varying depths. In such cases, changes in the thickness or surface position of the object can occur. Despite these challenges, software engineers require precise correspondence between imaging and actual dimensions.
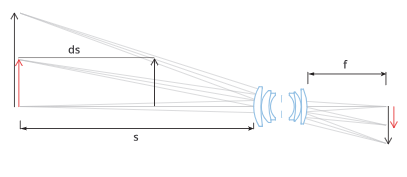
Standard lenses exhibit varying magnification at different conjugate positions. As a result, the image size of an object changes almost proportionally with its distance from the lens. This effect is easily observed in everyday life, such as when using a standard camera lens for photography.
Telecentric lenses, on the other hand, maintain consistent magnification across a defined range, typically referred to as the “depth of field” or “telecentric range.” This consistency ensures that variations in object position do not affect image size.
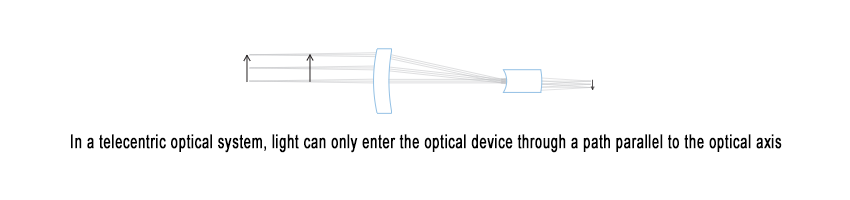
Telecentric lenses achieve this stability through their unique optical design. Only light rays that are parallel to the optical axis are captured by the objective, ensuring that the image size remains constant even as the object moves within the telecentric range. The diameter of the front lens must be at least as large as the diagonal of the object field to achieve this effect.
This optical behavior is achieved by precisely positioning the aperture stop at the focal plane of the front optical group. The incoming light appears to originate from an infinitely distant point, giving rise to the term “telecentric,” derived from the Greek words “tele” (distant) and “centre” (optical center).
To illustrate the difference between a standard lens and a telecentric lens, consider a standard lens with a focal length of 12 mm and a 1/3” detector, imaging an object of height H = 20 mm at a distance s = 200 mm. If the object moves by ds = 1 mm, the size change would be approximately:
dH = (ds/s) · H = (1/200) · 20 mm = 0.1 mm
For a telecentric lens, the magnification change depends on the “telecentric slope.” A high-quality telecentric lens typically has an effective telecentric slope of about 0.1° (0.0017 radians). In this case, the size change for a 1 mm object displacement would be:
dH = ds · θ = 1 · 0.0017 mm = 0.0017 mm
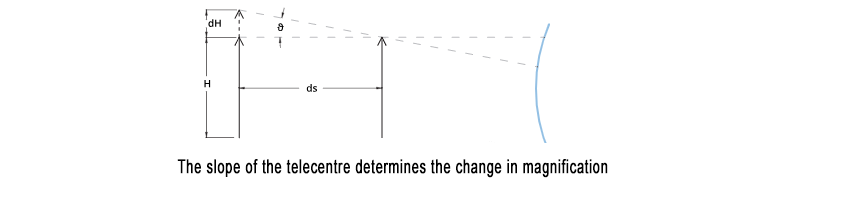
This results in an error reduction of 1/10 to 1/100 compared to a standard lens.
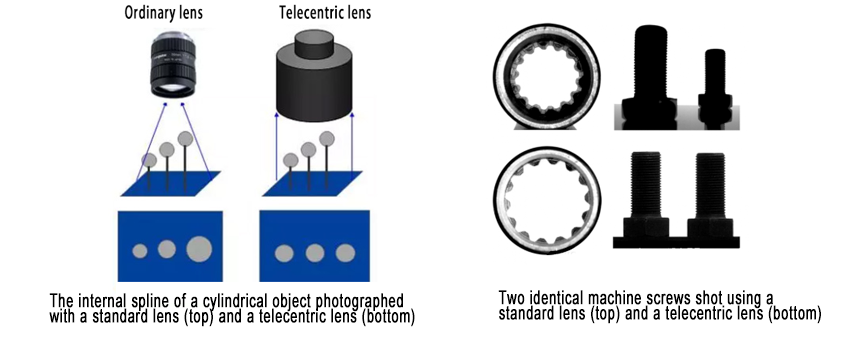
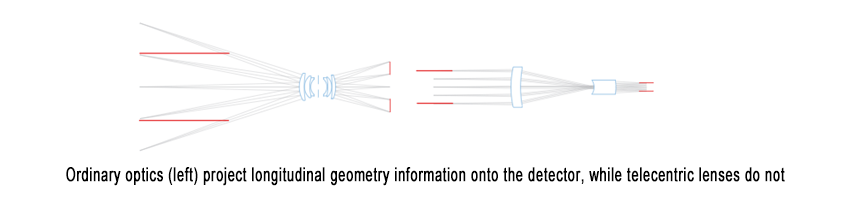
When using standard optics to image three-dimensional objects, distant parts appear smaller than closer ones. For example, when imaging a cylindrical cavity, the top and bottom edges appear as two concentric circles, even though they are identical in reality.
In contrast, telecentric lenses ensure that both edges overlap perfectly, with the bottom edge fully obscured. This effect is due to the specific light paths within the lens: while standard optics introduce vertical components of geometric information in the detector plane, telecentric lenses eliminate this distortion.
This makes telecentric lenses ideal for profile imaging and dimensional measurements, as they effectively suppress the third dimension of the object.
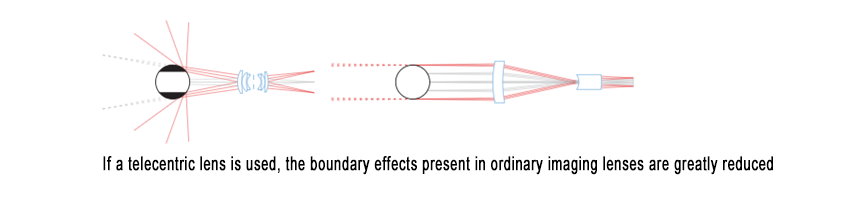
Determining the exact edge position of an object can be challenging, especially when backlighting is used. In such cases, bright pixels at the edge of the object may overlap with dark pixels, making it difficult to establish a clear boundary. Additionally, the three-dimensional shape of the object can further limit measurement accuracy.
For example, light rays grazing the object’s edge at an incident angle may reflect back into the lens, appearing to originate from behind the object. This can cause portions of the image to disappear, leading to inaccurate and unstable measurements.
Telecentric lenses effectively mitigate this issue by restricting the light rays that enter the lens to those that are nearly parallel to the optical axis. Since these rays are minimally deflected, the reflections from the object surface do not degrade measurement precision.
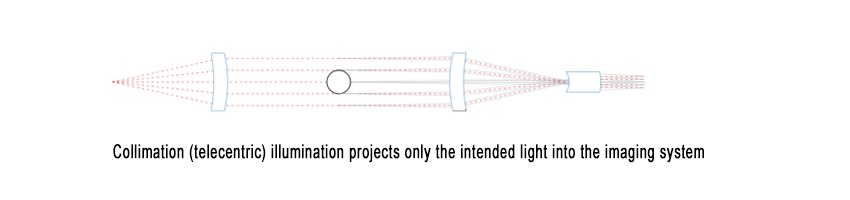
To fully address these challenges, a collimated (telecentric) illuminator can be paired with a telecentric lens. This setup ensures that all light from the illuminator is collected by the lens, achieving high signal-to-noise ratios and extremely short exposure times. Additionally, only “intended” light enters the imaging lens, eliminating edge ambiguity.
Bena Optics leverages its advanced assembly capabilities to enhance the performance of telecentric lenses. Our precision manufacturing processes ensure that each lens meets the highest optical standards, delivering exceptional stability and imaging quality.
By integrating state-of-the-art technologies such as ultra-precision alignment and advanced metrology, Bena Optics ensures that every telecentric lens is optimized for applications requiring magnification stability, perspective error reduction, and edge position certainty.
Whether for industrial metrology or advanced imaging systems, Bena Optics’ telecentric lenses offer unparalleled performance and reliability, setting new standards in precision optics.
Telecentric lenses, with their ability to maintain consistent magnification and reduce perspective errors, are essential tools in high-precision measurement and imaging applications. Bena Optics’ expertise in lens assembly ensures that these lenses deliver optimal performance, even in the most demanding environments.
By combining innovation with precision, Bena Optics continues to push the boundaries of optical technology, providing solutions that redefine what is possible in telecentric imaging.