Endoscope optical systems are critical components in medical and industrial applications, enabling detailed visual inspection of hard-to-reach areas. These systems are composed of three main parts: the objective lens, the relay lens group, and the eyepiece. Each component plays a specific role in capturing, transmitting, and amplifying images for clear visualization.
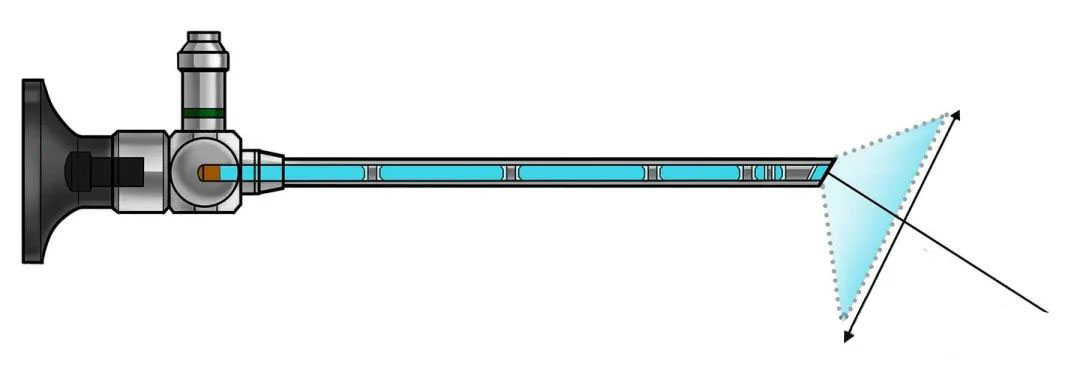
An endoscope optical system typically consists of the following components:
1. Objective Lens:
· Role: Determines the view angle (DOV) and field of view (FOV) of the endoscope. It captures images of the target object.
· Material: Often made of sapphire for durability and clarity.
2. Relay Lens Group:
· Role: Transmits the captured image from the objective lens to the eyepiece. It ensures the image remains in focus and undistorted during transmission.
3. Eyepiece:
· Role: Amplifies the image for clear viewing and transmits it through the eyepiece or display system.
Objective Lens: Captures the initial image of the target object, defining the endoscope’s view angle and field of view.
Relay Lens Group: Ensures the image is smoothly transmitted from the objective lens to the eyepiece without loss of detail or distortion.
Eyepiece: Magnifies the image and delivers it to the viewer's eye or an external display system.
4. View Angle (DOV):
· Definition: The angle formed between the incident light entering the objective lens and the horizontal line. This angle determines the direction and width of the view.
· Typical Angles: Endoscopes often feature view angles of 0°, 12°, 30°, 70°, and 90°.
· 0°: Provides a straight-ahead view for precise inspection.
· 12°–30°: Slightly angled views for targeted observations.
· 70°–90°: Wide-angle views suitable for broad areas or deep inspections.
5. Field of View (FOV):
· Definition: The range or area that the objective lens can observe. It determines the scope of the inspection.
· Types:
· Wide Angle (Broad FOV): Suitable for large cavities, such as in laparoscopes, hysteroscopes, and cystoscopes.
· Standard Angle (Narrow FOV): Ideal for small or precise inspections, such as in transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) surgeries.
6. Medical Applications:
· Laparoscopes: Wide-angle endoscopes used for abdominal surgeries.
· Hysteroscopes: Wide-angle endoscopes for gynecological inspections.
· Cystoscopes: Wide-angle endoscopes for bladder examinations.
· TURP Endoscopes: Standard-angle endoscopes for precise prostate surgeries.
7. Industrial Applications:
· Wide-Angle Endoscopes: Used for inspecting large machinery or structures.
· Standard-Angle Endoscopes: Employed for detailed inspections in confined spaces.
Endoscope optical systems are essential for providing clear, detailed visualizations in medical and industrial applications. The objective lens, relay lens group, and eyepiece work together to capture, transmit, and amplify images, enabling precise inspections.
The view angle (DOV) and field of view (FOV) are critical factors in determining the suitability of an endoscope for specific applications. Wide-angle endoscopes are ideal for large cavities, while standard-angle endoscopes excel in small, precise inspections.
By understanding the design and functionality of endoscope optical systems, healthcare professionals and engineers can leverage these tools to improve diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency.
Bena Optics is a leading provider of high-quality optical component for endoscopes, including objective lenses, relay lens groups, and eyepieces. Our precision-engineered systems ensure superior image clarity, sharpness, and durability, making them ideal for medical and industrial applications.
With a focus on innovation and performance, Bena Optics’ endoscope optical systems are designed to meet the demanding requirements of modern endoscopy. Explore our range of advanced optical solutions and experience the difference that superior technology can make.
Endoscope optical systems are a testament to the power of precision engineering in medical and industrial applications. By delivering clear, detailed visualizations, they enable breakthroughs in diagnostics and inspections across industries.