Reflective prisms are essential components in optical systems, serving as alternatives to planar mirrors for altering light paths and controlling image orientation. Unlike planar mirrors, reflective prisms are designed as monolithic glass blocks with internal reflective surfaces, offering advantages in terms of stability, durability, and ease of alignment.
This article provides a detailed overview of reflective prisms, their types, and their applications in modern optical systems.
Structure and Function of Reflective Prisms
Reflective prisms consist of two or more planar reflective surfaces integrated into a single glass block. These surfaces are designed to reflect light internally, ensuring that the entire optical path remains contained within the prism.
Critical Angle and Total Internal Reflection (TIR): If the incident angle of light on the reflective surface is greater than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs, maintaining high optical efficiency without the need for additional coatings.
Metal Coating for Partial Reflection: In cases where some light rays fall below the critical angle, a reflective metal coating can be applied to the surface to ensure complete reflection.
Reflective prisms are preferred over planar mirrors in many applications due to their superior mechanical stability, reduced susceptibility to environmental degradation, and ease of integration into optical systems.
Types of Reflective Prisms
Reflective prisms can be broadly classified into three categories:
Simple Reflective Prisms
Wedge Prisms (Double-Reflection Prisms)
Compound Prisms (Multiple-Reflection Prisms)
Each type serves specific purposes in optical systems, depending on the desired light path and image orientation.
Simple Reflective Prisms
Simple reflective prisms are the most basic type, consisting of a single reflective surface. They are designed to alter the light path without introducing significant image inversion.
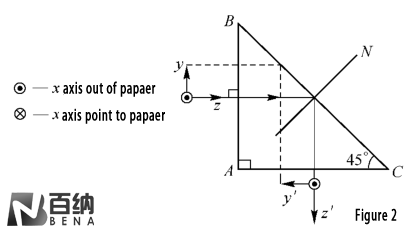
Iso-Rectangular Reflective Prism (Figure 2): The most common type, this prism features a 90° reflective surface that deflects the light path by 90°. It is widely used in optical systems where compactness and simplicity are required.
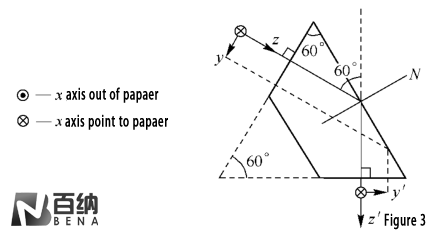
Equilateral Reflective Prism (Figure 3): This prism deflects the light path by 60° and can be designed for other deflection angles by adjusting the prism geometry.
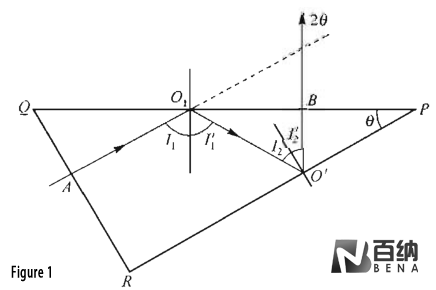
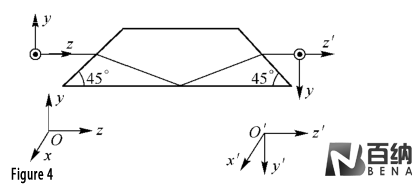
Dove Prism (Figure 4): A unique prism that alters the direction of light without changing its orientation. When rotated, the image produced by the prism rotates twice as much.
Wedge Prisms (Double-Reflection Prisms)
Wedge prisms consist of two reflective surfaces forming a dihedral angle. These prisms are used to achieve specific light path changes and are particularly useful in applications requiring precise deflection angles.
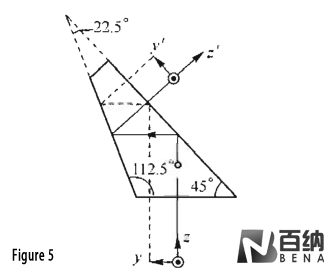
Half Penta Prism (Figure 5): With a dihedral angle of 22.5°, this prism deflects the light path by 45°. It is commonly used in microscope observation systems to redirect the light path for convenient viewing.
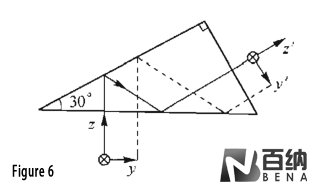
Right Angle prism: (Figure 6 )with a semi-pentagonal prism with two angles of 30° and an Angle of 60° between the incident light and the outgoing light. Right Angle prisms can also be used in observation systems in microscopes to turn the vertical axis of light into a direction for easy observation.
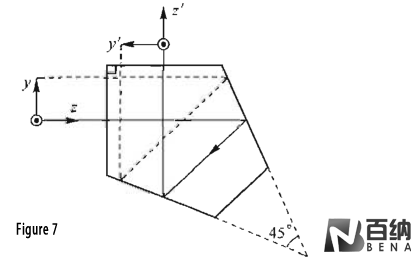
Penta Prism (Figure 7): Features a 45° dihedral angle, deflecting the light path by 90°. This prism is often used in place of a simple 90° reflective prism to avoid image inversion.
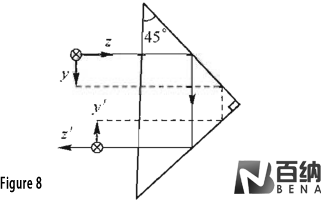
Double-Reflection Rectangular Prism (Figure 8): With a 90° dihedral angle, this prism deflects the light path by 180°, effectively reversing the direction of light. It is frequently used in image-inverting systems.
Compound Prisms (Multiple-Reflection Prisms)
Compound prisms involve multiple reflective surfaces and are designed for more complex light path manipulation. These prisms are particularly useful in applications requiring extended optical paths or specific image orientations.
Double reflection rectangular prism: (Figure 8 )with a double-reflection right Angle prism with two angles of 90° and an Angle between the incident light and the outgoing light of 180°. The shape of the prism is exactly the same as that of the single-reflection right Angle prism. Double reflection rectangular prisms are often used in image transfer systems.
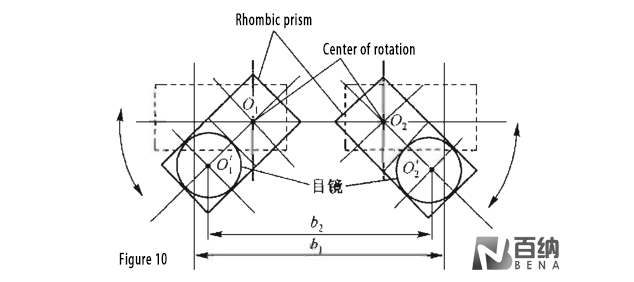
Rhombic prism: (Figure 9) shows a rhomb prism with two angles of 180° and an Angle of 360° between the incident light and the outgoing light, which can translate the optical axis. The rhombic prism is mostly used to adjust the program distance in binocular instruments. As shown in Figure 10, the rhombic prism has a common optical axis with a pair of eyepieces behind the exit plane of a pair of rhombic prisms, and takes the optical axis in front of the incident as the center line of the rotation axis of the rhombic prism, so that the two rhombic prisms can be reversed to adjust the eye distance. In Figure 10, b1 is the eye distance before adjustment and b2 is the eye distance after adjustment.
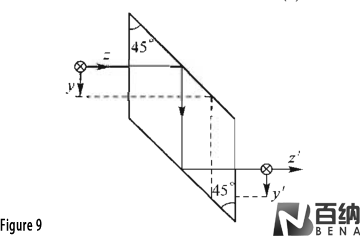
Figure 10: A pair of rhombic prisms to adjust the eye distance
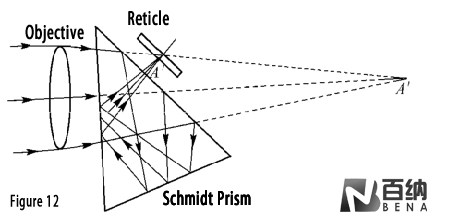
Schmidt Prism (Figure 11): A triple-reflection prism that deflects the light path by 45°. Its long optical path allows for the folding of light paths, reducing the overall size of optical systems.
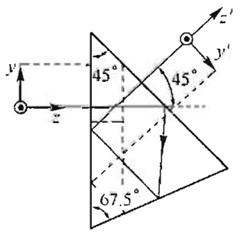
Figure 12: Folding optical path with Schmidt prism
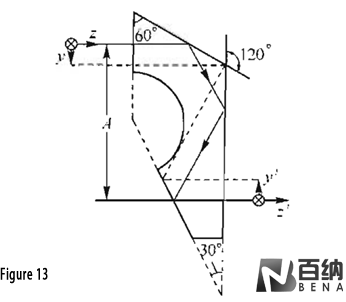
Leman Prism (Figure 13): Another triple-reflection prism that maintains the parallelism of the light path while introducing a lateral offset. This prism is used in applications requiring both alignment and separation of light paths.
Applications of Reflective Prisms in Optical Systems
Reflective prisms are widely used in a variety of optical instruments, including:
Telescopes and Binoculars: To redirect light paths and reduce the overall size of the instrument.
Microscopes: To adjust the viewing angle for better ergonomics.
Image Inversion Systems: To reverse or rotate images without altering their orientation.
Folding Optics: To compact long optical paths into smaller physical spaces.
Conclusion: The Versatility of Reflective Prisms in Modern Optics
Reflective prisms are indispensable components in modern optical systems, offering precise control over light paths, image orientation, and system compactness. From simple single-reflection prisms to complex multi-reflection designs, these components enable a wide range of applications in diverse fields, from scientific research to consumer electronics.
Bena Optics specializes in the design and manufacture of high-quality reflective prisms tailored to meet the specific needs of optical systems. Our prisms are engineered for precision, durability, and efficiency, ensuring optimal performance in a wide range of applications.
With a commitment to innovation and quality, Bena Optics is at the forefront of optical component development, providing reliable solutions for the most demanding optical challenges.
Reflective prisms are a cornerstone of modern optical systems, enabling precise control over light paths and image orientation.