Broadly speaking, any optical surface that is neither spherical nor planar is referred to as an aspheric surface. A spherical lens has a constant curvature from the center to the edge, while an aspheric surface's radius of curvature varies with its distance from the optical axis.
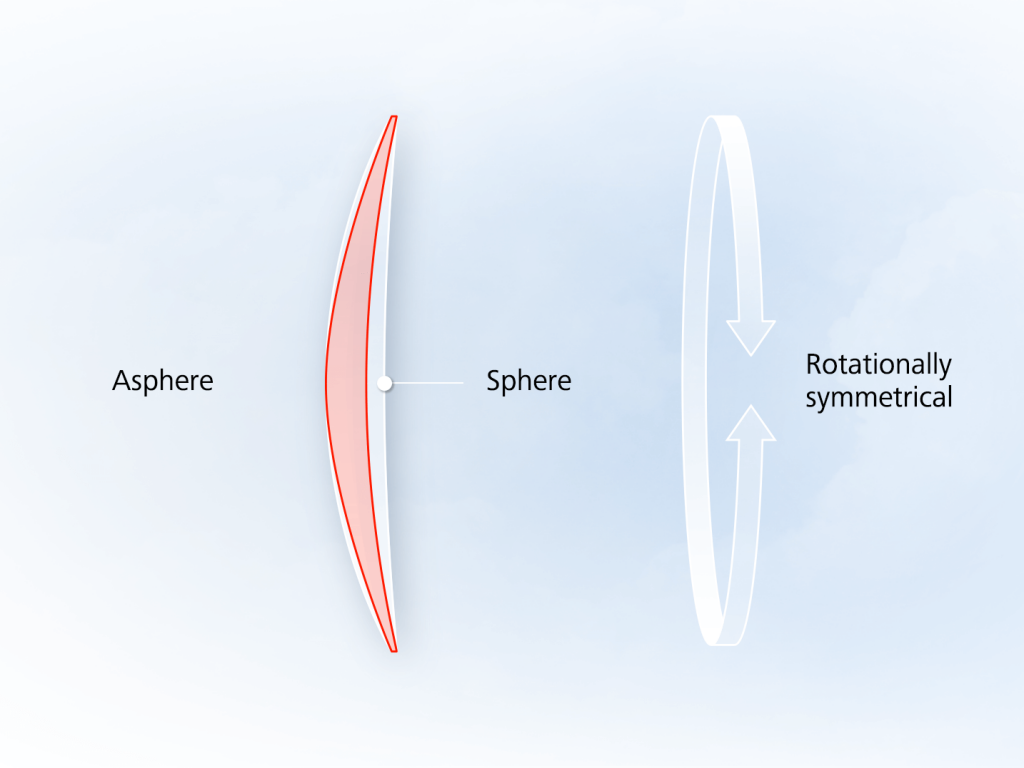
There are three main categories of aspheric surfaces used in optical systems:
Axisymmetric Aspheric Surfaces: Such as rotational conic surfaces and rotational higher-order surfaces.
Aspheric Surfaces with Two Symmetry Planes: Such as cylindrical and toric surfaces.
Freeform Surfaces: Which lack any symmetry.
Here, we specifically focus on rotational symmetric surfaces, which belong to the first category. Most applied aspheric surfaces fall into this group.
The most commonly used aspheric surface expression is based on a conic surface as a reference, superimposed with a series of higher-order polynomials. The expression is as follows:
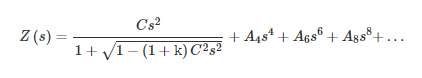

The actual conic surface produced will depend on the value and sign of the conic constant.
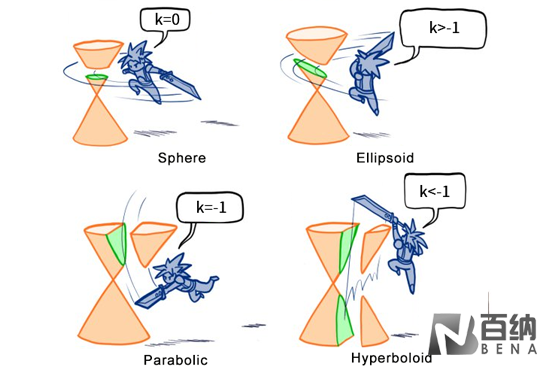
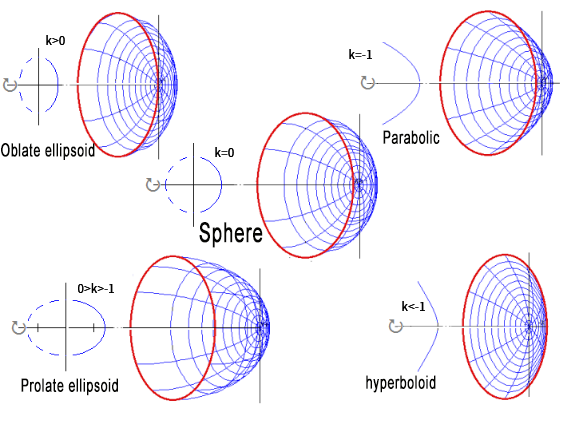
If it is difficult to relate the conic cross-section to the aspheric lens surface, the following diagram restores the cross-section into a 3D surface representation:
By understanding the principles of aspheric surfaces and their mathematical foundations, Bena Optics delivers cutting-edge optical solutions that address the challenges of modern laser and imaging applications.