Image sensors (such as CCD, CMOS, etc.) use a pixel array to sample and detect the image formed by an object through an objective lens, as shown in Figure 1.
![]()
Figure 1: Sampling of the signal by the pixel array Assume the pixel size of the image sensor is p, and the highest frequency sinusoidal signal measured by the system is sin[2π(x/d)], with a spatial period of d and a spatial frequency of ν(~)c=1/d. According to the sampling theorem, to accurately measure this signal, at least two pixels are required for one spatial period, one to sample the peak and one to sample the trough. Therefore,
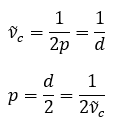
When using a pixel array in an image sensor, its cutoff frequency ν(~)c determines the system’s highest resolution. If the signal frequency is higher than the cutoff frequency ν(~)c, the sampling will be incomplete, and the set of sampled values cannot fully determine the signal. The reciprocal of the cutoff frequency ν(~)c, which is 2p, is the minimum resolvable length determined by the image sensor.
Bena Optics manufactures optical components in CCDs, such as spherical and aspherical lenses in CCS micro lenses, as well as dichroic filters, among others.