I. Introduction to Cylindrical Lenses
As the name suggests, cylindrical lenses possess at least one cylindrical surface. Unlike spherical lenses, which focus or disperse light uniformly in all directions, cylindrical lenses are designed to guide light along a single dimension. This unique functionality makes them invaluable for applications where other lenses cannot provide the required precision.
II. How Cylindrical Lenses Work
The distinctive shape of cylindrical lenses allows them to focus light from sources like lasers into a straight line. This ability to control light in a single dimension, whether compressing or expanding the beam, makes them extremely versatile. Their design enables precise bending and focusing of light to meet the specific needs of various applications.
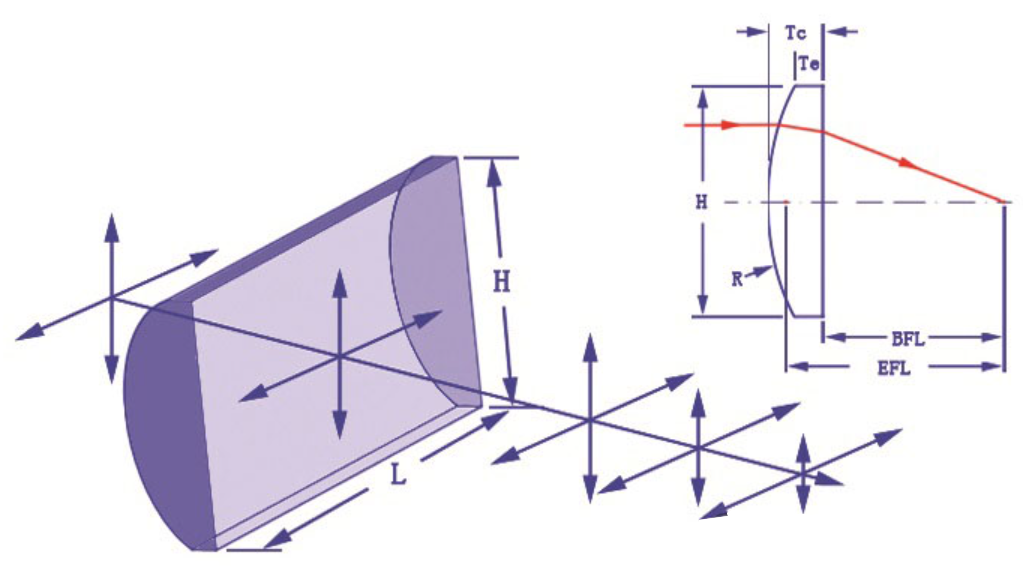
III. Types of Cylindrical Lenses
Plano-Convex Cylindrical Lenses: One surface is flat, and the other is convex.
Plano-Concave Cylindrical Lenses: One surface is flat, and the other is concave.
Double-Convex Cylindrical Lenses: Both surfaces are convex.
Double-Concave Cylindrical Lenses: Both surfaces are concave.
Meniscus Cylindrical Lenses: Shaped like a crescent, with one convex and one concave surface.
Cylindrical Cross Lenses: Featuring a unique crossed cylindrical structure.
Custom-Shaped Cylindrical Lenses: Non-standard shapes designed for specific requirements.
IV. Applications of Cylindrical Lenses
Correcting Astigmatism: Align with the astigmatic axis to focus light onto a single plane, correcting distorted or blurry images.
Laser Beam Shaping: Reshape laser beams, particularly in semiconductor lasers, to improve quality and achieve a circular profile.
Spectroscopy: Adjust the spatial and spectral characteristics of light in spectroscopy applications, such as diffraction gratings.
Laser Line Scanning: Shape laser beams into straight lines for applications like 3D metrology and quality control.
Microscopy: Improve confocal microscopy by shaping laser beams, correcting aberrations, and enhancing signal-to-noise ratios in fluorescence microscopy.
Note: Semiconductor laser tubes often emit elliptically shaped beams that require correction.
.png)
V. Industrial Uses of Cylindrical Lenses
Cylindrical lenses are widely applied across multiple industries:
Industrial Inspection: Essential for laser scanning systems, alignment tools, and laser processing equipment.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Critical for circularizing elliptical beams in wafer inspection tools and flat-panel display measurement systems.
Entertainment: Used in digital cinema cameras and projectors to compress or stretch images for optimal visual quality.
Life Sciences and Medical Fields: Crucial in life science imaging and medical diagnostic instruments.
These specialized optical tools play a critical role in directing light along a single dimension, with applications ranging from correcting astigmatism in ophthalmology to shaping laser beams to enhance performance. The diversity of available cylindrical lenses underscores their importance in advancing tools and technologies across multiple fields.
Cylindrical lenses, with their unique ability to control light in a single dimension, are indispensable in precision optics. From correcting astigmatism to shaping laser beams for high-performance applications, their versatility and precision make them a key component in a wide range of industries. With a variety of materials and design options available, cylindrical lenses continue to drive innovation in optics and beyond.